Hi-van is supported by its audience. When you purchase using our links, we may earn an affiliate commission (no added cost to you). Learn more
The primary purpose of space blankets is to reflect thermal radiation. These slender and lightweight blankets are now widely used in healthcare emergencies, survival gears, and outdoor adventures. Space blankets can retain and reflect heat, but do they keep things cold?

Space blankets can keep things cold by preventing heat transfer through radiation, convection, and evaporation. However, space blankets cannot prevent heat transfer through conduction. Thus, your cold material will get warm in contact with a heat source.
The original space blankets, also known by a trademark Mylar, and the commercially available survival or emergency blankets are not identical. A particular variety’s ability to keep things cold or hot depends on the blanket’s properties. Let’s discuss these features of space blankets.
How Do Space Blankets Block Thermal Radiation?
NASA designed the first space blankets using a special type of polyester film developed jointly by DuPont, presently known as DowDuPont; the now-defunct Imperial Chemical Industries; and Hoechst AG, which is currently a subsidiary of Sanofi.
The polyester film is known as BOPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate). Companies use molten polymer that undergoes biaxial orientation and subsequent metalization.
The final plastic is a strong and durable yet flexible barrier with chemical and electrical insulation properties. The metalized coating serves as the infrared-reflective component.
NASA uses vaporized aluminum to vacuum-metalize the plastic and calls it silver insulation.
BOPET and metalized aluminum’s reflectivity make space blankets effective at blocking thermal radiation. A space blanket with an insulative coating on each side can reflect thermal or infrared radiation from either or both ways.
In a nutshell, a commercially available space blanket of reasonable quality can keep external or environmental heat out. Also, a space blanket can retain heat if you flip the side with reflective coating and seal it impeccably or use a variety that has insulation on both surfaces.
However, the heat transfer through conduction is still at play.
Thermal Radiation vs. Conduction vs. Convection
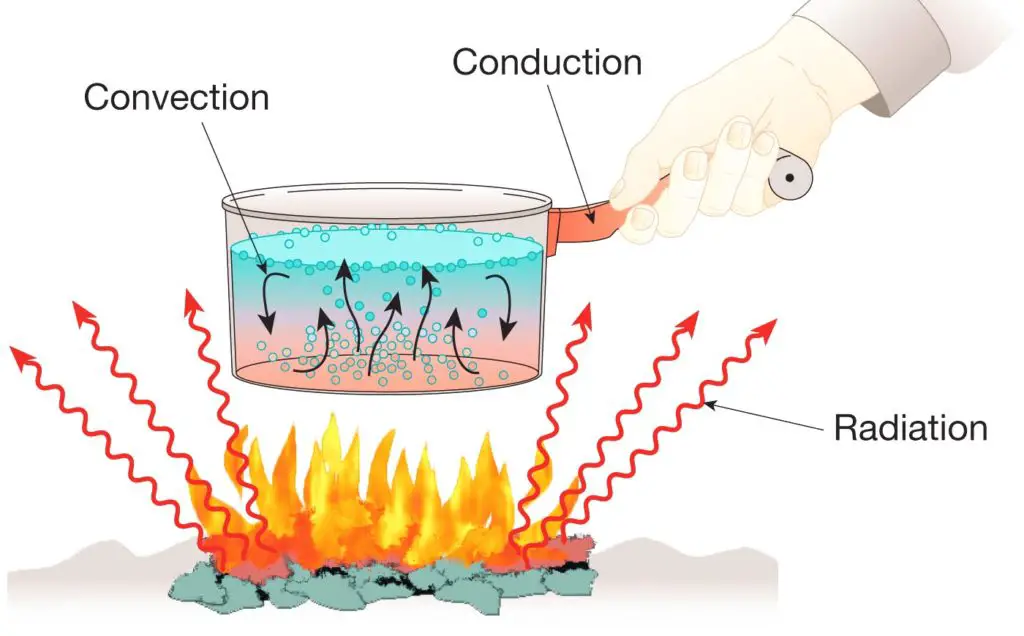
Thermal radiation does not require any particular medium for heat transfer. Infrared or electromagnetic radiation causes heat to transfer through air and space or vacuum.
Conduction needs a medium for heat transfer, usually, contact. Convection needs a medium, too, typically a fluid, like air.
Space blankets are excellent barriers to thermal radiation. Premium-quality space blankets can prevent convection heat transfer, subject to how well you seal the material. If there is any gap, hole, or opening for airflow, a space blanket will not prevent or stop convection heat transfer.
Conduction is a completely different story. A space blanket will not provide sufficient insulation from heat transfer through contact. Thus, the heat transfer through conduction will happen if you wrap a cold object with a space blanket and keep it on a hot surface.
Similarly, suppose you want to keep something warm and place the space blanket on a cold surface. In that case, the object will get cooler until it reaches a temperature or thermal equilibrium, as defined by the zeroth law of thermodynamics.
The Laws of Thermodynamics
Darkness is the absence of light. Likewise, cold is the absence of heat.
According to the first and second laws of thermodynamics, a cold object cannot make another material cooler by transferring its degree of coldness. The relatively warmer material can transfer its heat to the colder object, and it gets cooler in the process.
Space blankets do not generate heat or cold. They are only barriers. A hot or cold object will not remain warm or cool perpetually if the interacting environment is not in a state of thermal or thermodynamic equilibrium.
Thus, if a space blanket must keep something cold, the setting must be a cooler, chiller, refrigerator, or freezer. Also, the space blanket must be vacuum-sealed to prevent airflow. Convection heat transfer will happen if air finds its way through the wrapping or packaging.
Furthermore, a space blanket must be used as a complete wrap to keep anything cold or hot. Otherwise, heat transfer will happen through electromagnetic radiation through any part of an object not covered by the reflective and insulating space blanket.
Space Blanket vs. BOPET Packaging for Foods & Perishables
The various composite films you find in the packaging of food products are essentially BOPET. You see these films in the containers of plenty of everyday grocery items, such as:
- Mayonnaise
- Pasta
- Breakfast cereals
- Snacks
- Crackers
- Tea
- Coffee
- Frozen items
BOPET is also used for medical products, perfumes, and other things.
Space blanket comprises BOPET, but the latter is not necessarily the former. Companies have distinct formulas for their BOPET or composite films. Toray Industries Inc. has its trademarks.
Retal Group has its varieties. SABIC has its innovative takes.
BOPET packaging and space blanket are not interchangeable. Besides, packaging for foods and perishables, whether frozen or fresh, requires cold or vacuum packing with self-sealing adhesives. A space blanket wrapped around a person or cold object is not sealed that way.
Space Blanket’s Insulation on Earth
Space blankets are too thin and ineffective at preventing heat transfer through conduction to be a suitable insulating material on earth. Also, our planet has various environmental factors, such as rain, snow, wind, and sunlight.
A space blanket can reflect the heat radiated by the sun. Thus, a person or an object exposed to sunlight will be cooler when covered in a space blanket. However, convection through gaps and conduction through touch or contact will cause heat transfer and influence the temperature.
Companies making space blankets for emergencies, outdoor or survival gear, and other purposes typically use additional materials for better insulation against heat or cold.
Can be used as a ground tarp, shelter, tent, or emergency blanket when camping, hunting, backpacking, or boating. Keep one in the trunk of your car for the unexpected!
The Arcturus Heavy Duty Survival Blanket, available on Amazon.com, is an insulated thermal reflective tarp that uses two layers of polypropylene for waterproofing. However, the infrared thermal barrier is on one side only.
- Aluminized Mylar
- Lightweight and durable
- Designed to retain up to 90% of your body heat
- 100% money-back guarantee
The Swiss Safe Emergency Mylar Thermal Blankets from Amazon.com have aluminized coating on both sides. These space blankets are designed for NASA, hence making them fitting for first aid or emergency, survival gears, and outdoor adventures.
Interestingly, even the space blankets designed for NASA officially claim the ability to retain up to 90% of body heat during emergency use. Hence, some heat transfer will happen, and a warm or cool object will lose heat or coldness, respectively.
Conclusion
Theoretically and practically, space blankets are not designed to keep things cold. You may use them as barriers to prevent heat transfer through radiation and convection if impeccably sealed. The internal temperature within a space blanket is still subject to the laws of thermodynamics.
If you wish to keep anything cold or cool, the ambiance inside and around the space blanket should be appropriate. Otherwise, blocking electromagnetic radiation alone will not keep the object or person cool perpetually.
Find this content useful 🙂 ?
Subscribe to our Newsletter and get a free Solar Electric Diagram + shopping list.